CAPM Mock Test: Our CAPM® mock exam is designed for entry-level professionals, project coordinators, and analysts who want to test their knowledge and strengthen their project management fundamentals. This mock test covers key areas like project integration, scope, schedule, cost, quality, communication, and risk management — fully aligned with the latest CAPM® exam standards. Use this practice exam to assess your readiness, identify improvement areas, and build confidence to ace the CAPM® certification exam on your first attempt!
CAPM Mock Test 6 – 150 Practice Questions
This is the 6th installment of our CAPM® Mock Test Series! Designed for entry-level professionals, project coordinators, and analysts, this free mock exam helps you practice key project management concepts across all major domains. Aligned with the latest CAPM® exam standards, this test is perfect for assessing your readiness and boosting your confidence for the real exam.
The CAPM® exam syllabus is structured around the PMI’s Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) and focuses on the fundamental principles and practices of project management. Key topics include project integration, scope, schedule, cost, quality, resource, and communication management. Candidates are also expected to understand project risk, procurement, and stakeholder management, along with a strong grasp of professional ethics and responsibility. Each domain is designed to build a solid foundation in managing projects using globally recognized standards.
In addition to these knowledge areas, the syllabus emphasizes project life cycles, organizational structures, and the role of a project manager. It covers tools and techniques used in planning, executing, monitoring, and closing projects. The CAPM® syllabus also reflects the growing importance of agile and adaptive project environments, providing insights into how traditional and modern project management methods can be applied. By mastering this syllabus, candidates will be well-equipped not only to pass the certification exam but also to apply practical skills in real-world projects.
CAPM Mock Test 6
Below is the 6th part of our CAPM® Mock Test Series, featuring 150 carefully crafted questions drawn from the core areas of the CAPM® exam syllabus. These questions are designed to reflect real exam difficulty and cover topics such as project integration, scope, schedule, cost, quality, communication, and risk management.
CAPM Mock Test 6
Quiz-summary
0 of 25 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
Information
CAPM Mock Test 6
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 25 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- CAPM 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 25
1. Question
What is “Control Changes” about?
Correct
Control Changes is the process of reviewing, approving, and managing all change requests.
Incorrect
Control Changes is the process of reviewing, approving, and managing all change requests.
-
Question 2 of 25
2. Question
What does an emergent product backlog mean?
Correct
An emergent product backlog refers to a dynamic list of features, enhancements, and bug fixes that evolves throughout the project. In agile methodologies, especially Scrum, the backlog is continuously refined as new information, feedback, or changing priorities are incorporated. This ensures that the product remains aligned with stakeholder needs and business goals, allowing flexibility and adaptability during development.
Incorrect
An emergent product backlog refers to a dynamic list of features, enhancements, and bug fixes that evolves throughout the project. In agile methodologies, especially Scrum, the backlog is continuously refined as new information, feedback, or changing priorities are incorporated. This ensures that the product remains aligned with stakeholder needs and business goals, allowing flexibility and adaptability during development.
-
Question 3 of 25
3. Question
What type of project team structure allows for shared leadership and decision-making responsibilities?
Correct
Distributed Management allows for shared leadership and decision-making responsibilities across the project team. This structure empowers team members to take on leadership roles and participate in decision-making, rather than having a single, centralized authority (PMBOK Guide 7th Edition, page 17).
Incorrect
Distributed Management allows for shared leadership and decision-making responsibilities across the project team. This structure empowers team members to take on leadership roles and participate in decision-making, rather than having a single, centralized authority (PMBOK Guide 7th Edition, page 17).
-
Question 4 of 25
4. Question
Which of the following is not a method of schedule compression?
Correct
The schedule baseline is the approved version of a schedule model that can be changed using formal change control procedures and is used as the basis for comparison to actual results (PMBOK Guide 7th Edition, page 249).
Incorrect
The schedule baseline is the approved version of a schedule model that can be changed using formal change control procedures and is used as the basis for comparison to actual results (PMBOK Guide 7th Edition, page 249).
-
Question 5 of 25
5. Question
In Agile projects, what mechanism helps the team determine if work items can be worked on?
Correct
In adaptive approaches, the “definition of ready” is a series of conditions that the entire team agrees to complete before a user story is considered sufficiently understood so that work can begin. This helps the project team know when the user story is sufficiently elaborated and ready to be worked on.
Incorrect
In adaptive approaches, the “definition of ready” is a series of conditions that the entire team agrees to complete before a user story is considered sufficiently understood so that work can begin. This helps the project team know when the user story is sufficiently elaborated and ready to be worked on.
-
Question 6 of 25
6. Question
What type of approach is typically used in a predictive project life cycle to handle project deliverables?
Correct
In a predictive life cycle, the project deliverables, scope, time, and cost are defined early on in the project, and any changes are controlled carefully. This type of project management is typically plan-driven, where detailed upfront planning is essential, and the team follows the predefined plan closely to manage scope, deliverables, and changes.
Incorrect
In a predictive life cycle, the project deliverables, scope, time, and cost are defined early on in the project, and any changes are controlled carefully. This type of project management is typically plan-driven, where detailed upfront planning is essential, and the team follows the predefined plan closely to manage scope, deliverables, and changes.
-
Question 7 of 25
7. Question
What distinguishes leadership from management?
Correct
Leadership is primarily about inspiring, motivating, and influencing people to achieve a vision or common goal. In contrast, management is focused on planning, organizing, and controlling processes to ensure the efficient and effective completion of tasks and objectives (PMBOK Guide 7th Edition, page 17).
Option A: Leadership is not about processes, but rather about people.
Options C & D: Management focuses on executing tasks and controlling resources, while leadership is more about inspiring and motivating.
Incorrect
Leadership is primarily about inspiring, motivating, and influencing people to achieve a vision or common goal. In contrast, management is focused on planning, organizing, and controlling processes to ensure the efficient and effective completion of tasks and objectives (PMBOK Guide 7th Edition, page 17).
Option A: Leadership is not about processes, but rather about people.
Options C & D: Management focuses on executing tasks and controlling resources, while leadership is more about inspiring and motivating.
-
Question 8 of 25
8. Question
What role does the project manager take on when helping team members develop their skills and supporting their professional growth?
Correct
When a project manager helps team members develop their skills and supports their professional growth, they are acting as a coach. This role involves mentoring, providing feedback, and encouraging personal development to enhance the team’s overall capabilities.
Incorrect
When a project manager helps team members develop their skills and supports their professional growth, they are acting as a coach. This role involves mentoring, providing feedback, and encouraging personal development to enhance the team’s overall capabilities.
-
Question 9 of 25
9. Question
Which of the following is not considered a typical relationship that a business analyst manages?
Correct
While a business analyst works with various team members like quality control teams for reviewing requirements, developing a working relationship with a Quality Assurance (QA) Manager is not typically within the direct scope of relationship management. QA roles are more focused on product testing rather than contributing to the business analysis or stakeholder engagement processes. Thus, while interaction may occur, this relationship is not managed in the same capacity as those with sponsors or functional managers.
Incorrect
While a business analyst works with various team members like quality control teams for reviewing requirements, developing a working relationship with a Quality Assurance (QA) Manager is not typically within the direct scope of relationship management. QA roles are more focused on product testing rather than contributing to the business analysis or stakeholder engagement processes. Thus, while interaction may occur, this relationship is not managed in the same capacity as those with sponsors or functional managers.
-
Question 10 of 25
10. Question
Which activity is typically conducted during the project close phase to capture lessons learned?
Correct
During the project close phase, retrospectives are typically conducted to capture lessons learned. This activity allows the project team to reflect on what went well, what could be improved, and how to apply those lessons to future projects.
Option C: Project scope review focuses on ensuring that all deliverables were completed
Option D: Team performance evaluations assess individual and team performance but are not specifically for gathering lessons learned.
Incorrect
During the project close phase, retrospectives are typically conducted to capture lessons learned. This activity allows the project team to reflect on what went well, what could be improved, and how to apply those lessons to future projects.
Option C: Project scope review focuses on ensuring that all deliverables were completed
Option D: Team performance evaluations assess individual and team performance but are not specifically for gathering lessons learned.
-
Question 11 of 25
11. Question
Which of the following tools is associated with managing project schedules?
Correct
A Gantt Chart is a tool used to manage and visualize project schedules. It displays the timeline of tasks, their durations, dependencies, and progress, making it an effective tool for tracking project timelines.
Incorrect
A Gantt Chart is a tool used to manage and visualize project schedules. It displays the timeline of tasks, their durations, dependencies, and progress, making it an effective tool for tracking project timelines.
-
Question 12 of 25
12. Question
What is typically required for determining whether all or part of a solution should be released?
Correct
A release decision is essential for determining whether all or part of a solution should be released. It includes formal acceptance or rejection of the solution based on its readiness and adherence to requirements, as evidenced by the evaluated acceptance results, product risk analysis, and readiness assessment (PMI Guide to business analysis, page 298).
Incorrect
A release decision is essential for determining whether all or part of a solution should be released. It includes formal acceptance or rejection of the solution based on its readiness and adherence to requirements, as evidenced by the evaluated acceptance results, product risk analysis, and readiness assessment (PMI Guide to business analysis, page 298).
-
Question 13 of 25
13. Question
The project team cannot plan for risks that are believed to be difficult to find or imagine. Therefore, a(n) ___________ reserve should be set for threats that were not identified in advance.
Correct
The Management Reserve is a budget under “management control” that is dedicated and used for risks that were not identified during risk analysis, aka unknown-unknowns (unknown = unidentified, unknowns = risks).
Option C: A contingency reserve is used for identified risks with predetermined risk response strategies, aka known-unknowns (known = identified, Unknowns = risks) (PMBOK 7th edition, page 127).
Options B & D: Additional reserve and buffer reserve are made-up terms.
Incorrect
The Management Reserve is a budget under “management control” that is dedicated and used for risks that were not identified during risk analysis, aka unknown-unknowns (unknown = unidentified, unknowns = risks).
Option C: A contingency reserve is used for identified risks with predetermined risk response strategies, aka known-unknowns (known = identified, Unknowns = risks) (PMBOK 7th edition, page 127).
Options B & D: Additional reserve and buffer reserve are made-up terms.
-
Question 14 of 25
14. Question
A business analyst is tasked to determine the scope of a new product. However, some stakeholders are resistant to change and question the project’s added value. What should the business analyst do to address stakeholder concerns? (Select two)
Correct
A stakeholder engagement plan ensures that the concerns of stakeholders, particularly those resistant to change, are addressed proactively. By identifying key stakeholders and tailoring communication strategies, the business analyst can foster better relationships and ensure that stakeholders see the project’s value. Additionally, A business case analysis helps clarify the project’s value by demonstrating how it aligns with business objectives and provides benefits to the organization (PMI Guide to business analysis, page 124).
Option D: A competitive analysis focuses on obtaining and analyzing information about an organization’s external environment. It doesn’t address stakeholder concerns about the project’s added value.
Option E: A transition plan is more useful later in the project, when moving to a new solution, rather than addressing initial concerns about the project’s value during initiation.
Incorrect
A stakeholder engagement plan ensures that the concerns of stakeholders, particularly those resistant to change, are addressed proactively. By identifying key stakeholders and tailoring communication strategies, the business analyst can foster better relationships and ensure that stakeholders see the project’s value. Additionally, A business case analysis helps clarify the project’s value by demonstrating how it aligns with business objectives and provides benefits to the organization (PMI Guide to business analysis, page 124).
Option D: A competitive analysis focuses on obtaining and analyzing information about an organization’s external environment. It doesn’t address stakeholder concerns about the project’s added value.
Option E: A transition plan is more useful later in the project, when moving to a new solution, rather than addressing initial concerns about the project’s value during initiation.
-
Question 15 of 25
15. Question
Which of the following is an example of a project constraint?
Correct
Explanation
A constraint is something that limits the project’s options or actions, such as a restricted schedule due to vendor availability.Incorrect
Explanation
A constraint is something that limits the project’s options or actions, such as a restricted schedule due to vendor availability. -
Question 16 of 25
16. Question
What is the main goal of a standup meeting?
Correct
Explanation
Standup meetings are short, frequent (usually daily) meetings designed to quickly update the team on progress, identify obstacles, and keep everyone aligned.Incorrect
Explanation
Standup meetings are short, frequent (usually daily) meetings designed to quickly update the team on progress, identify obstacles, and keep everyone aligned. -
Question 17 of 25
17. Question
Which change management element involves checking if new capabilities are having the intended impact?
Correct
Implementing change is an iterative element that focuses on demonstrating the future state capabilities, checking to ensure the capabilities are having the intended impact, and making necessary improvements or adaptations in response (PMBOK Guide 7th Edition, page 161).
Incorrect
Implementing change is an iterative element that focuses on demonstrating the future state capabilities, checking to ensure the capabilities are having the intended impact, and making necessary improvements or adaptations in response (PMBOK Guide 7th Edition, page 161).
-
Question 18 of 25
18. Question
How does poor communication between a business analyst and the technical team impact the project? (Select two)
Correct
Poor communication between the business analyst and the technical team often results in misinterpretation of requirements, leading to incorrect deliverables. This can cause rework, driving up project costs and causing delays.
Option B: Even with unclear requirements, the project manager should follow the Integrated Change Control process to prevent scope creep.
Incorrect
Poor communication between the business analyst and the technical team often results in misinterpretation of requirements, leading to incorrect deliverables. This can cause rework, driving up project costs and causing delays.
Option B: Even with unclear requirements, the project manager should follow the Integrated Change Control process to prevent scope creep.
-
Question 19 of 25
19. Question
When facilitating requirements gathering, why must a business analyst effectively communicate with both technical and non-technical teams?
Correct
Communication is essential to bridge the gap between technical and non-technical teams, ensuring that both technical and non-technical teams are aligned on business goals (what the project needs to achieve) and technical limitations (what is feasible given the available technology and resources). (PMI Guide to business analysis, page 49)
Option C: A business analyst’s role is not primarily to manage the technical team’s pace but to ensure clear communication about the requirements and goals of the project.
Option D: While effective communication may reduce the need for extra meetings, this is not the main reason for a business analyst to bridge communication gaps between teams.
Incorrect
Communication is essential to bridge the gap between technical and non-technical teams, ensuring that both technical and non-technical teams are aligned on business goals (what the project needs to achieve) and technical limitations (what is feasible given the available technology and resources). (PMI Guide to business analysis, page 49)
Option C: A business analyst’s role is not primarily to manage the technical team’s pace but to ensure clear communication about the requirements and goals of the project.
Option D: While effective communication may reduce the need for extra meetings, this is not the main reason for a business analyst to bridge communication gaps between teams.
-
Question 20 of 25
20. Question
A project manager is in the process of monitoring the results of the execution of the quality management activities. What can the project manager use to perform the process effectively?
Correct
As defined in the Process groups guide (page 179), inspection is a main tool for the control quality process.
Options B, C, D: Project management information system, Expert judgment, and Change control tools are not tools for the control quality process.
Incorrect
As defined in the Process groups guide (page 179), inspection is a main tool for the control quality process.
Options B, C, D: Project management information system, Expert judgment, and Change control tools are not tools for the control quality process.
-
Question 21 of 25
21. Question
One month into the project, the sponsor contacts the project manager to express dissatisfaction with the project work. The sponsor says that deliverables match neither the requirements nor the set expectations. What should the project manager do?
Correct
Project scope verification or control involves reviewing deliverables to make sure that each is appropriately completed as per requirements. Any discovered inconsistency or dissimilarity should be rectified before seeking the sponsor’s formal approval through the “validate scope” process.
Incorrect
Project scope verification or control involves reviewing deliverables to make sure that each is appropriately completed as per requirements. Any discovered inconsistency or dissimilarity should be rectified before seeking the sponsor’s formal approval through the “validate scope” process.
-
Question 22 of 25
22. Question
Which project risk listed in the table below is most likely to occur?
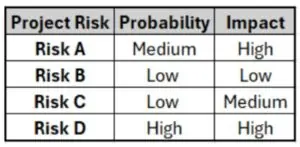 Correct
Correct
The most likely risk is the one with the highest probability score.
Incorrect
The most likely risk is the one with the highest probability score.
-
Question 23 of 25
23. Question
Shortly after acquiring the resources, the project manager discovers that the team members are politically very engaged; almost all of their meetings end with a political dispute between team members. The project manager has decided to put an end to this before it deteriorates team members’ relationships, by prohibiting any political discussions. Where should the project manager note this rule?
Correct
The team charter is the right document to include rules and guidelines on how the team members should interact with each other (Agile Practice Guide, page 20 & PMBOK 7th edition, page 192). By adding the rule to the team charter, team members will have to adhere to it and refrain from discussing politics at work.
Option B: The project charter includes a brief description of the project and its requirements. The resource charter is a made-up term.
Option D: The Resource management plan, on the other hand, covers staffing acquisition, timetable, training needs, recognition and rewards, release criteria, compliance, and safety.
Incorrect
The team charter is the right document to include rules and guidelines on how the team members should interact with each other (Agile Practice Guide, page 20 & PMBOK 7th edition, page 192). By adding the rule to the team charter, team members will have to adhere to it and refrain from discussing politics at work.
Option B: The project charter includes a brief description of the project and its requirements. The resource charter is a made-up term.
Option D: The Resource management plan, on the other hand, covers staffing acquisition, timetable, training needs, recognition and rewards, release criteria, compliance, and safety.
-
Question 24 of 25
24. Question
What is the major difference between lessons learned and retrospectives?
Correct
Retrospectives are typically conducted at regular intervals, such as after each iteration or sprint in agile methodologies. This allows the team to reflect on recent work, make improvements, and adjust the process continuously throughout the project.
Incorrect
Retrospectives are typically conducted at regular intervals, such as after each iteration or sprint in agile methodologies. This allows the team to reflect on recent work, make improvements, and adjust the process continuously throughout the project.
-
Question 25 of 25
25. Question
What is the key advantage of using document analysis in requirements gathering?
Correct
Explanation
Document analysis involves reviewing existing documents, contracts, reports, or any relevant written information to gather requirements. By doing so, stakeholders don’t need to spend as much time in face-to-face meetings, as a significant amount of data can already be gathered through the documents.Incorrect
Explanation
Document analysis involves reviewing existing documents, contracts, reports, or any relevant written information to gather requirements. By doing so, stakeholders don’t need to spend as much time in face-to-face meetings, as a significant amount of data can already be gathered through the documents.

